Script Forms
WARNING
The Script API is currently in active development, and breaking changes are frequent. This page assumes the format of Minecraft 1.20.60
In version 1.18.30, Minecraft released a wonderful new script module, @minecraft/server-ui (formerly named mojang-minecraft-ui). With this module, we can create form UIs without the need for JSON UI-wrangling.
Setup
Like other modules, you will need to add the dependency into your manifest.json
{
"dependencies": [
{
"module_name": "@minecraft/server-ui",
"version": "2.0.0"
},
{
"module_name": "@minecraft/server",
"version": "1.9.0-beta"
}
]
}And import the module on your script files
import { ActionFormData, MessageFormData, ModalFormData } from "@minecraft/server-ui";Form Type
The @minecraft/server-ui module comes with 3 form types- the Action Form Data, Message Form Data, and Modal Form Data.
ActionFormData
Action Form is the form which contains a bunch of buttons. This form is ideal for shop UIs, minigames selections, etc. If you have seen a featured server has a UI with lots of buttons, this is that form.
To use the form, you need to create it first.
let form = new ActionFormData();The form has 3 functions/properties: Title, Body, and Button.
Title
Title is a text on the top of the form.
form.title("Action Form");Body
Body adds some sort of description of the form. You can explain more about the function of the form.
form.body("This is Action Form Body");Button
Button is the main function of the form. The form can have many buttons for the player to choose. Each button has 2 arguments. The first argument is the label, the text that shows up on the button.
The second argument is optional and is the button icon, which shows a picture/icon on the button. To use it, you need to define the texture path. You can use the vanilla resource pack to show icons (Example textures/items/compass). Custom textures will need .png at the end of the path, as well as a valid resource pack on the world.
// No icon
form.button("Button 1");
// With vanilla texture
form.button("Button 2", "textures/items/compass");
// With custom texture
form.button("Button 3", "textures/icon/btn_icon_3.png");WARNING
The maximum number of buttons is 256. More may cause the form to break.
Example
This an example of an Action Form.
let form = new ActionFormData();
form.title("Minigames");
form.body("Choose the games");
form.button("Spleef", "textures/items/diamond_shovel");
form.button("Murder Mystery", "textures/items/iron_sword");
form.button("Bedwars", "textures/minigames/bedwars.png");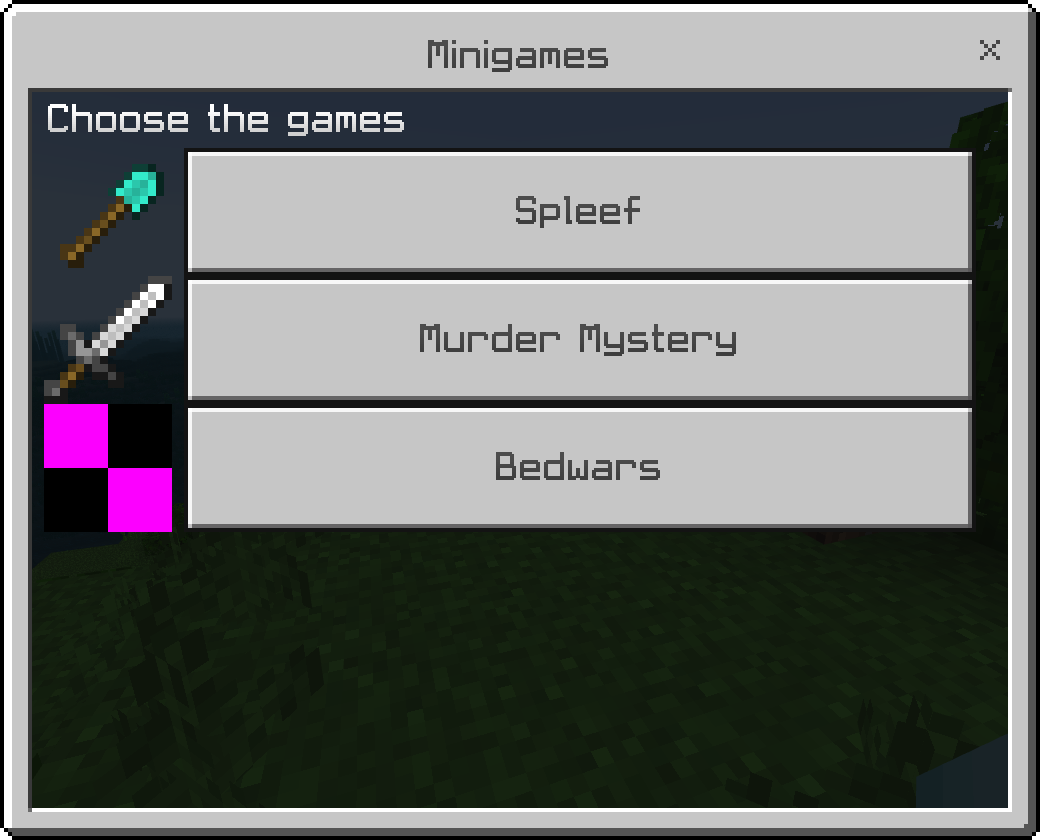
MessageFormData
Message form is a form that consists of 2 buttons with a large description (body). This form is great for Yes/No questions or OK/Cancel forms.
let form = new MessageFormData();The Message Form is very similar to the Action Form. The main difference is that the buttons are called Button1 and Button2 instead.
Title
Title is the text on the top of the form.
form.title("Message Form");Body
Body adds some sort of description of the form. You can explain more about the function of the form.
The body text limit on a Message Form is huge, so you can fit 5+ lines of text there. To add a new line, use \n.
form.body("This is Message Form Body");Button1 and Button2
Message Form only contains 2 buttons, unlike Action Forms, which can have more than 2 buttons. This form was created to give a warning or message to players.
Just like the buttons on an Action Form, button1 and button2 have 2 arguments, text and icon.
form.button1("Button 1: No");
form.button2("Button 2: Yes");TIP
Because the Message Form only has 2 buttons, it's recommended to have "Yes/OK" option on "button2" and "No/Cancel" option on "button1". You can see the problem in the "Show and Respond" section
Example
This is an example of a Message Form
let form = new MessageFormData();
form.title("Higher Random Tick Warning");
form.body(
"Are you sure you want to run this command:\n/gamerule randomtickspeed 1000\nThis can cause lag to the world"
);
form.button1("No, leave it as default!");
form.button2("Yes, do it!");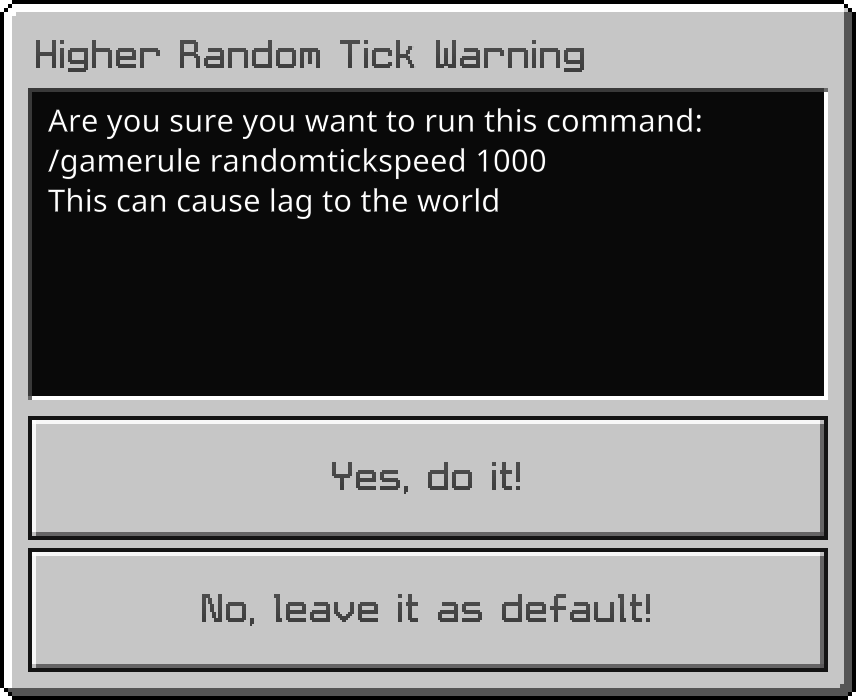
ModalFormData
Modal Form has the most types of input available in the form. It has text fields, sliders, dropdowns, and toggles. Modal forms are useful for complicated forms, such as an effect giver. Modal forms don't have a body property.
let form = new ModalFormData();Modal Form has 5 properties: Title, Text field, Dropdown, Slider, and Toggle.
Title
Title is a text on the top of the form.
form.title("Modal Form");Text Field
Text field is a property that allows the player to insert text. It has 3 arguments.
- Label (
Str), the title for the text field. - Placeholder Text (
Str), some sort of description or info for the text field. - Default Value (
Str)[Optional], the default text in the text field. Default is empty (null).
// Without default value
form.textField("Text Field", "Type something here");
// With default value
form.textField("Text Field", "Type something here", "Default value");Dropdown
Dropdown is a property that contains a list options. It has 3 arguments.
- Label (
Str), the title for the dropdown. - Options (
List[String]), the list of the options for the player to choose from. - Default Value Index (
Int)[Optional], the index of the default value. Default is0(first item in the list).
Dropdowns are also unique in that they don't return the value of whatever the option is, rather, they return the number of the option. For example, the first option will return "0", the second "1", etc. This way, options can be mapped to their respective values behind-the-scenes, and have different display text from values.
// Internal Options
form.dropdown("Dropdown", ["Opt 1", "Opt 2", "Opt 3"], 1);
// Default Index "1" will select the second option ("Opt 2") as default option
// External Options (Recommended)
let options = ["Opt 1", "Opt 2", "Opt 3"];
form.dropdown("Dropdown", options);Slider
Slider is a property that can hold a range of numbers. It has 5 arguments.
- Label (
Str), the title for the slider. - Min Number (
Int), the lowest number of the range. - Max Number (
Int), the highest number of the range. - Value Step (
Int), the step value of the range. - Default Value (
Int)[Optional], the default number of the slider. Default is the lowest number.
// Normal range from 1 to 100
form.slider("Slider", 1, 100, 1);
// Even number from 0 to 10 with default value set as 10
form.slider("Slider", 0, 10, 2, 10);Toggle
Toggle is a property that only has a true/false option. It has 2 arguments.
- Label (
Str), the title for the toggle. - Optional toggleOptions (
Dict), which allows setting default value and tooltip
form.toggle("Toggle", {
defaultValue: true,
});Example
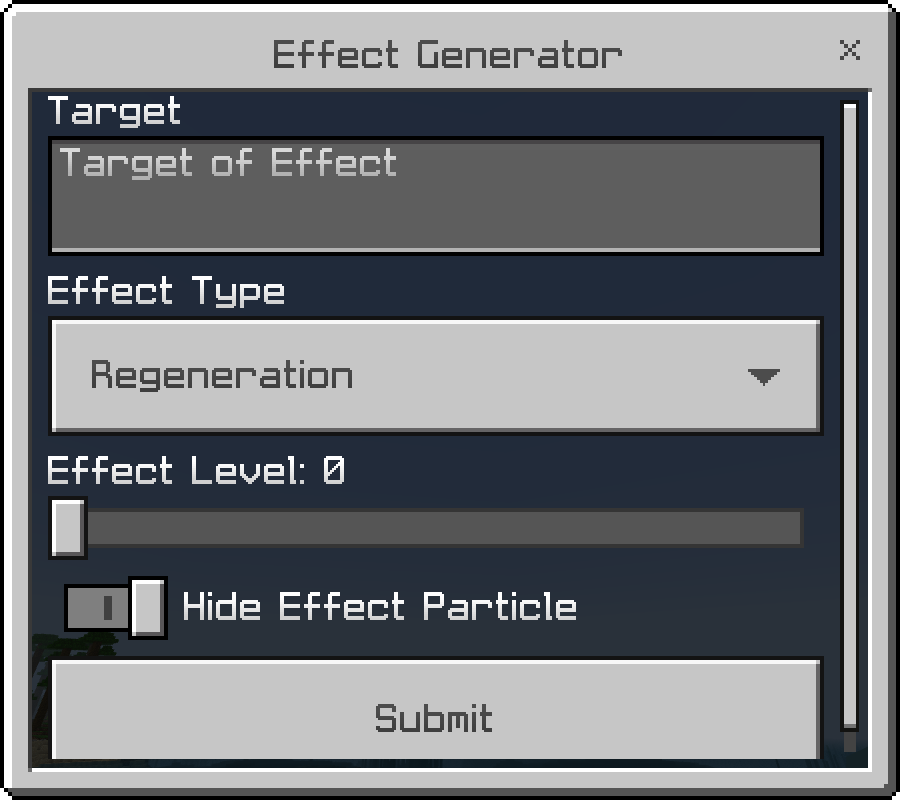
This is an example of a Modal Form with all of the components
let form = new ModalFormData();
let effectList = ["Regeneration", "Protection", "Poison", "Wither"];
form.title("Effect Generator");
form.textField("Target", "Target of Effect");
form.dropdown("Effect Type", effectList);
form.slider("Effect Level", 0, 255, {
defaultValue: 1,
});
form.toggle("Hide Effect Particle", {
defaultValue: true,
});
Show and Respond
After we create the form, we will need to show the form to the player and save the response to run other tasks. We will need some event to show our form. The most used event is using itemUse event, that reads when a player uses (right-clicks) an item.
Let's say our form must be opened with a stick that is named "Form Opener". You can use any event with any configurations in order to open your own form.
world.beforeEvents.itemUse.subscribe((event) => {
if (event.itemStack.typeId === "minecraft:stick" && event.itemStack.nameTag === "Form Opener") {
// Form
}
});WARNING
These forms will only open when no other UI is open. If you want to open the form through a custom command/chat message, you cannot because the chat UI is open. You will need to use /damage to close the chat UI, then open the form. The best option is using another event.
Inside the if statement is where our form will be shown. Using .show(), the form will open. Inside the show function, you will need a player class as an argument. After we show the form, we can use .then() to save the response of player.
form.show(event.source)
.then((r) => {
// The code when the player responds to/closes the form
})
.catch((e) => {
console.error(e, e.stack);
});When player closes the form, the function inside the .then() will run, even if no input was given. This can cause unintended code to run when player just closes the form. To prevent that, you will need to cancel the script using .canceled.
form.show(event.source)
.then((r) => {
// This will stop the code when the player closes the form
if (r.canceled) return;
// The code when the player responds to the form
})
.catch((e) => {
console.error(e, e.stack);
});Finally, we can do something with the player input. Every form has their own return input from the player.
ActionFormData
Action form saves the input inside .selection. It returns a number of the button index, starting from 0 as button 1. You can use switch-case to run certain code for every button.
form.show(event.source)
.then((r) => {
// This will stop the code when the player closes the form
if (r.canceled) return;
let response = r.selection;
switch (response) {
case 0:
// Do something when button 1 is pressed
// Don't forget "break" for every case
break;
case 1:
// Do something when button 2 is pressed
break;
// You can add cases for each button
default:
// Use this when your button doesn't have a function yet
// You don't need to use "break" on default case
// Remember to place the default on very bottom
}
})
.catch((e) => {
console.error(e, e.stack);
});MessageFormData
Similar to the action form, the message form will save the input inside .selection. Clicking .button1 will return 0, and clicking .button2 will return 1. Although there is no close button, pressing 'Escape' will close the form. We can use .canceled to handle this event.
form.show(event.source)
.then((r) => {
if (r.canceled || r.selection == 0) {
// Do something when the player closes the form or presses "button1"
return;
}
//we don't need to test for "r.selection == 1" since that the only case we didn't handle yet.
// Do something when player presses "button2"
})
.catch((e) => {
console.error(e, e.stack);
});ModalFormData
Modal forms save the input inside .formValues as a list of inputs. The inputs are sorted from the top-most component to the bottom-most component.
For example
let form = new ModalFormData();
form.textField(...);
form.dropdown(...);
form.slider(...);
form.toggle(...);
// ...
console.warn(r.formValues);
// Output: [ <TextField Input>, <Dropdown Input>, <Slider Input>, <Toggle Input> ]Because the form will output based on what component is on the top first, you can assign each input into its own variable.
let form = new ModalFormData();
form.textField(...);
form.dropdown(...);
form.slider(...);
form.toggle(...);
form.show(event.source).then(r => {
// This will stop the code when the player closes the form
if (r.canceled) return;
// This will assign every input their own variable
let [ textField, dropdown, slider, toggle ] = r.formValues;
// Do something
}).catch(e => {
console.error(e, e.stack);
});










