Understanding Selectors
Target selectors are used in commands to target who you want to execute a command on without explicitly setting a target, such as a player's name. A target selector is comprised of a selector variable, and optionally a list of selector arguments.
Selector Variables
The selector variable defines the broad list of entities to select. There are six selector variables to choose from:
@a- Target all players@p- Target the nearest player@r- Target a random player@e- Target all entities@s- Target the executor@initiator- Target the player interacting with an NPC
Selector Arguments
Selector arguments can narrow down a list of target candidates to those who meet certain conditions. In order to use selector arguments, you must first have a selector variable. To start with selector arguments you must add square brackets [] to the end of the chosen target selector like this: kill @e[]. Multiple selector arguments can be used by separating them with commas.
Type
Limits the selection of targets by their identifier. Negating the argument selects entities without that identifier. This argument cannot be repeated unless negated, since a given entity can only have one identifier. This argument can be used with the selector @r to select entities randomly.
type=<identifier>—Include only entities with the given identifier.type=!<identifier>—Exclude any entities with the given identifier.
Examples:
Affect all pigs with levitation:
/effect @e[type=pig] levitation
Kill all entities that are not arrows and snowballs:
/kill @e[type=!arrow,type=!snowball]
Count
Limits the number of selected entities, following selector sorting rules.
The selectors @a, @p, and @e sort by increasing distance, while @r sorts randomly. For the variables @p and @r, this argument defaults to 1. Negating this argument reverses the sorting order; random sorting cannot be negated.
c=<count>—Select up to<count>entities.
Examples:
Clear stone from the closest five players:
/clear @a[c=5] stone
Damage the furthest two skeletons:
/damage @e[type=skeleton,c=-2] 2
Position
Changes the position a selector starts its search at. It also modifies where the distance and volume arguments are positioned. Leaving any undefined defaults to the command's current position.
Relative coordinates can be used to define a relative offset from the command's position.
x=<value>,y=<value>, andz=<value>—Defines a position for the target selector.
Examples:
Teleport the closest player to (140, 64, -200) ten blocks up:
/teleport @p[x=140,y=64,z=-200] ~ ~10 ~
Distance
Limits the selection of targets by their spherical distance from the selector. This selects entities by their feet.
rm=<value>andr=<value>—Selects entities between the minimum and maximum number of blocks away, inclusive and respectively.
Examples:
Kill all chickens between two and six blocks away:
/kill @e[type=chicken,rm=2,r=6]
Enchant the held item with Sharpness for all players within one block of (0, 100, 0):
/enchant @a[x=0,y=100,z=0,r=1] sharpness
Volume
Limits the selection of targets to those within or intersecting a specified cuboid volume (bounding box). There are three arguments, each determining the size of the box along their respective axes. If at least one argument is defined, any remaining arguments left undefined are assumed to be 0. This selects entities by their hitbox.
The general formula for calculating the volume between two positions can be viewed as:
dx = x2 - x1
dy = y2 - y1
dz = z2 - z1dx=<value>,dy=<value>, anddz=<value>—Selects entities inside the given bounding box.
Examples:
List all entities within a 12x30x2 box:
/say @e[dx=12,dz=30,dy=2]
Add the "wiki:lobby" tag to all players between (-400, 0, -350) and (-150, 256, 50):
/tag @a[x=-400,y=0,z=-350,dx=250,dy=256,dz=400] add wiki:lobby
Add the "wiki:warp" tag to all entities between (-1.5, 0, -2) and (1, 0, 1.5):
/tag @a[x=-1.5,y=0,z=-2,dx=2.5,dz=3.5] add wiki:warp
NOTE:
The target will still be selected even if their hitbox is only partially contained within the volume.
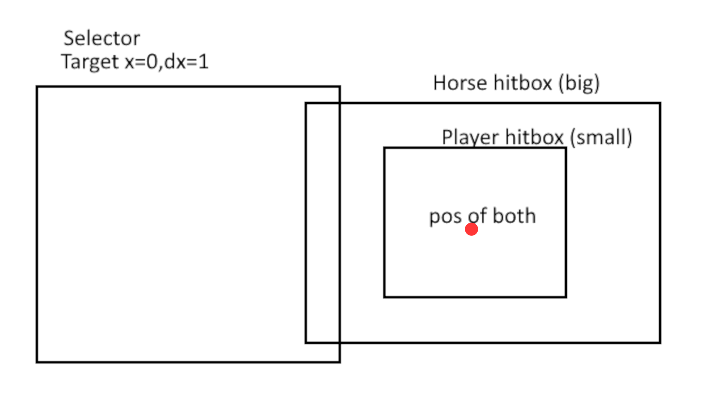
In this visual representation, we can see that the horse with a larger hitbox is selected, while the player with a smaller hitbox is not selected, despite standing at the same point.
Considering the above note, if we want to detect players exactly at a certain Y level (e.g., Y=10) and not partially, we can use a command like this:
/execute as @a at @s if entity @s[y=10,r=1] unless entity @s[y=9,r=1] run say found player
Scores
Limits the selection of targets by their score value. This argument is represented as an object, with key-value pairs for a scoreboard objective and a value. The value can represent a range of numbers, using the range syntax. The value of a score can be negated to test if the entity does not have a score value within that range.
scores={<objective>=<value>}—Selects entities whose score under the given objective matches the given value.
The range syntax works as follows:
N..is any number greater than or equal to N...Nis any number less than or equal to N.N..Mis any number between N and M, inclusive.
Examples:
Set the "points" score for all players with a "wiki:points" score of ten to 0:
/scoreboard players set @p[scores={wiki:points=10}] wiki:points 0
Add the "wiki:start" tag to armor stands with both a "wiki:started" score of one, and a "wiki:timer" score of 20 or less:
/tag @e[type=armor_stand,scores={wiki:started=1,wiki:timer=..20}] add wiki:start
Name
Limits the selection of targets by name. Negating the argument selects entities whose name does not match.
name=<name>—Include only entities with the given name.name=!<name>—Exclude any entities with the given name.
Examples:
List all zombies named Shadow:
/say @e[type=zombie,name="Shadow"]
Give one level to players both not named Steve and not named Alex:
/xp 1L @a[name=!"Steve",name=!"Alex"]
Tag
Limits the selection of targets by their tags. This argument can be repeated to test for multiple tags, and all filters must pass for an entity to be selected. Negating this argument selects entities without that tag.
tag=<tag>—Include only entities with the given tag.tag=!<tag>—Exclude any entities with the given tag.
Examples:
Kill all mobs with the tag "wiki:marked", and without the tag "wiki:exempt":
/kill @e[tag=wiki:marked,tag=!wiki:exempt]
Family
Limits the selection of targets by type family. This argument can be repeated to test for multiple families, and all filters must pass for an entity to be selected. Negating this argument selects entities whose type family does not match.
family=<family>—Include only entities with the given type family.family=!<family>—Exclude any entities with the given type family.
Examples:
Affect all entities in the "monster" family with Regeneration:
/effect @e[family=monster] regeneration
Property
Limits the selection of targets by property. This argument can be repeated to test for multiple families, and all filters must pass for an entity to be selected. Negating this argument selects entities whose property does not match. Properties can be defined in the Entity Behavior file, and various from types (bool, int, enum,..etc based on behavior set-up)
has_property={key=value}- Include only entities with the correct propertyhas_property=!{key=value}- Excludes any entities with the correct propertyExamples Kill all entities with wiki:property=true:
/kill @e[has_property={wiki:property=true}]
Rotation
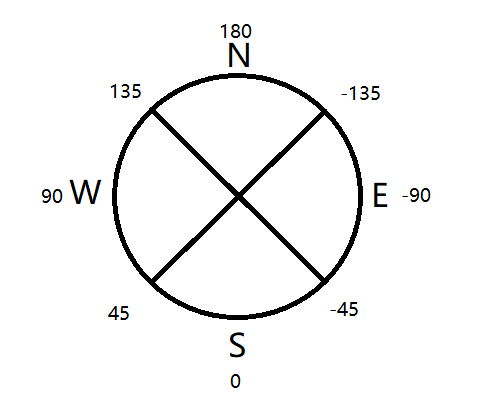
Limits the selection of targets by their rotation. There are two types of rotation: x-rotation, which is vertical rotation around the x-axis; and y-rotation, which is horizontal rotation around the y-axis. X-rotation ranges between -90 and 90 (180° total), going from looking up to down; and y-rotation ranges between -180 and 180 (360° total), starting and ending at North, wrapping around clockwise.
rxm=<value>andrx=<value>—Selects entities whose x-rotation is between the minimum and maximum values, inclusive and respectively.rym=<value>andry=<value>—Selects entities whose y-rotation is between the minimum and maximum values, inclusive and respectively.
x-rotation diagram shared by @SpacebarNinja:
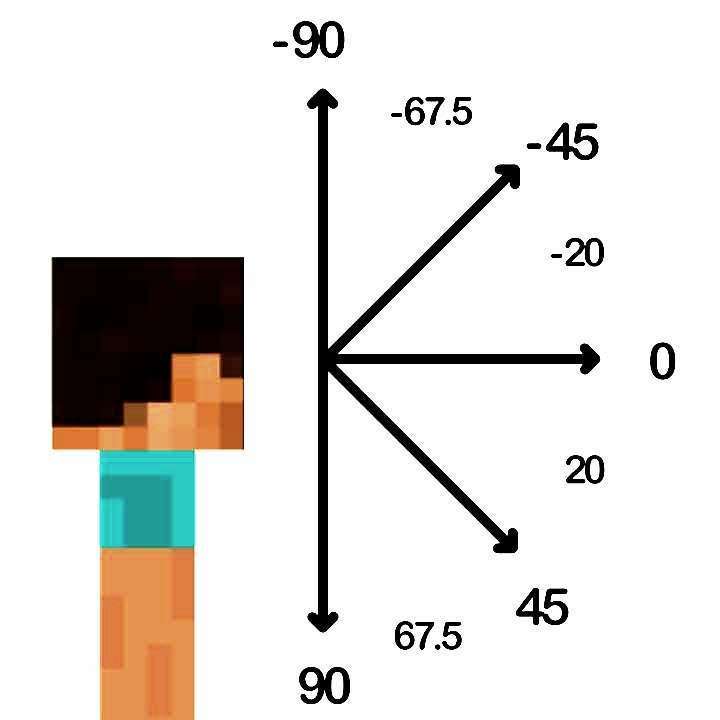
y-rotation diagram shared by @SpacebarNinja:
Examples:
Affect all players looking at or above the horizon with Blindness for one second:
/effect @a[rx=0] blindness 1(0 or less)
Damage all players facing generally south:
/damage @a[rym=-45, ry=45] 1
All Facing Directions:
| Facing Direction | Range (ry,rym) |
|---|---|
| North | [ry=-135,rym=135] |
| South | [ry=45,rym=-45] |
| East | [ry=-45,rym=-135] |
| West | [ry=135,rym=45] |
| North West | [ry=180,rym=90] |
| North East | [ry=-90,rym=-180] |
| South West | [ry=90,rym=0] |
| South East | [ry=0,rym=-90] |
Useful Articles Related to the Rotation Arguments:
Level
Limits the selection of targets by experience levels. Only players can have EXP, so this filters out non-player targets.
lm=<amount>andl=<amount>—Selects players whose EXP levels are between the minimum and maximum values specified, inclusive and respectively.
Examples:
Give all players who have nine or less levels a gold ingot:
/give @a[lm=9] gold_ingot
Give all players who have ten or more levels a gold ingot:
/give @a[l=10] gold_ingot
Give all players who have between ten and twenty levels a diamond:
/give @a[lm=10, l=20] diamond
Game Mode
Limits the selection of targets by game mode. Only players can use game mode, so this filters out non-player targets. Negating the argument selects targets whose game mode does not match.
m=<gamemode>—Selects players by their game mode.
All Game Mode Values:
| Game Mode | Values |
|---|---|
| Survival | 0, s, survival |
| Creative | 1, c, creative |
| Adventure | 2, a, adventure |
| Spectator | spectator |
| Default | d, default |
Examples:
List all players in Creative mode:
/say @a[m=creative]
Set the game mode to Creative mode for players both not in Survival mode, and not in Adventure mode:
/gamemode creative @a[m=!survival,m=!adventure]
Items
Limits the selection of targets by what items they have in their inventory. This argument is represented as an object, or an array of objects, with up to one each of the following parameters:
item=<string>—The identifier of the item to test for, and the only required argument. This can accept custom identifiers too.quantity=<int>—The amount of the item to test for. Accepts a range for a value. This argument can also be negated.data=<int>—The data value of the item to test for. Defaults to -1. Currently not functional: MCPE-151920location=<string>—The slot the item should be located in. Accepts the same arguments as the slotType argument in the/replaceitemcommand.slot=<int>—The index of the slot used in the "location" argument, and can only be used with "location". Accepts a range for a value. This argument can be negated.
Examples:
Checks for players who have a netherite sword in their inventory:
/testfor @a[hasitem={item=netherite_sword}]
Clears 2 apples for players that have four or more apples:
/clear @a[hasitem={item=apple,quantity=4..}] apple 2
Checks for players who have two sticks and two diamonds:
/testfor @a[hasitem=[{item=diamond,quantity=2},{item=stick,quantity=2}]]
Checks for players who doesn't have a stick:
/testfor @a[hasitem=[{item=stick,quantity=0}]








